Amazon EKS Workshop > Advanced > Observability with AWS Distro for Open Telemetry > Deploy Backend Microservices
Deploy Backend Microservices
Deploy Backend Microservices
The microservice we are going to deploy looks like this one:
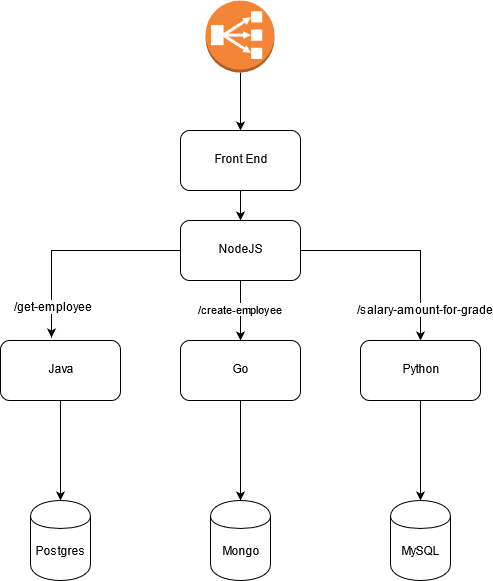
Grab a copy of the microservices:
git clone https://github.com/overdrive3000/adot-demo.git
cd adot-demo
Deploy the microservice’s databases into your EKS Cluster:
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/databases/
Quickly, check all the database services are deployed and ready to receive requests:
Deploy the backend services:
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/backend/
In the backend service manifest, we specified an ingress with ELB Load Balancer. Let’s wait until the ELB is fully deployed:
If you do not see an External-IP, re-run the command and wait till it shows (this can take a minute or two)